Non-surgical treatment of periodontal disease
When teeth start to move and gums start to recede: it’s up to us!
Periodontitis or periodontal disease is an infectious disease characterised by the destruction of the supporting tissues around one or more teeth. Periodontitis is mainly caused by the accumulation of tartar and biofilm (dental plaque) under the gums.
Treatment of non-surgical periodontal disease at CHD
The hygienist will systematically carry out a complete check-up of your mouth to verify the progress of periodontitis and the absence of any other problems. As periodontitis is often linked to other systemic diseases, this is a good time to discuss with your hygienist whether periodontitis may be affecting your general health.

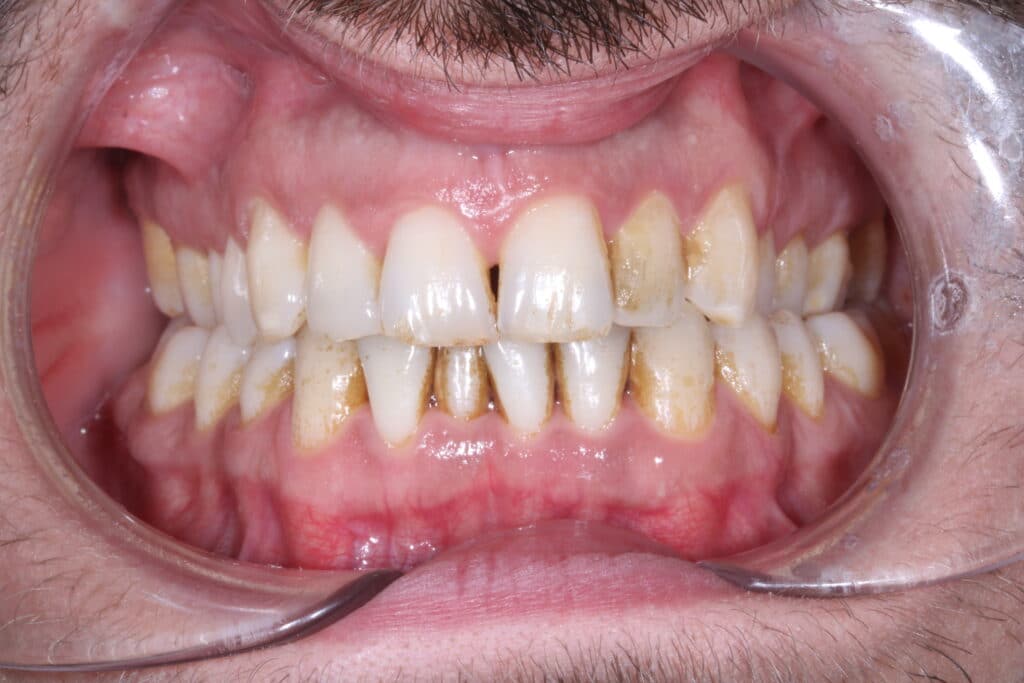
The supporting tissues gradually detach from the tooth and the space between the tooth and the gum deepens, leading to mobility and loosening of the teeth (which appear longer).
Periodontal disease is particularly difficult to detect because it is painless. If regular monitoring is not carried out, it is often too late to diagnose it (you consult your dentist because your teeth are moving or your gums have receded). What’s more, once the disease has stabilised, it requires regular, in-depth treatment throughout your life.
There are usually three phases to periodontitis: early (or mild), moderate and advanced.
Visit our library of
Rates
| Treatment by quotation |
Price varies according to the number of curettage sessions required.
*You can pay by invoice and pay in instalments.
Fair & transparent prices
We strive to maintain unbeatable value for money: reasonable prices, which have not changed since 2016, for quality of care that has earned us numerous awards:



Advice
At the end of the session, you will be given oral hygiene advice to help prevent the appearance of plaque and maximise the effectiveness of your periodontal disease treatment.
Periodontal disease is difficult to detect because it is not painful. If it is not regularly monitored, it is often diagnosed too late. It is also a disease which, once it has stabilised, required regular treatment and maintenance for life.
Dr Lagouge, Periodontologist CHD Meyrin
Next appointment
Your next appointment (recall) is scheduled as part of the personalised follow-up offered by CHD. This is based on your lifestyle, the quality of your saliva and other parameters, to ensure that your oral health remains at an optimum level. And you don’t have to worry about it any more, we’ll take care of reminding you: text message, letter, email, it’s your choice!
Our dental clinics
Find out more about periodontal disease
At CHD, how do you manage the disease?
1. Initial scaling to reduce superficial inflammation.
2. Oral hygiene instructions to teach you how to clean your teeth properly and prevent the recurrence of dental plaque.
Tip: Brushing your teeth is unfortunately not enough!
3. Probing or measuring the pockets in your entire mouth.
This provides a roadmap of your mouth, showing the exact location of periodontal pockets and enabling you to follow up by comparing the progress of these pockets: very useful.
4. Deep cleaning under local anaesthetic to remove tartar from the roots of the teeth and bacteria-infected tissues in the periodontal pockets.
Note: the number of sessions is case-dependant
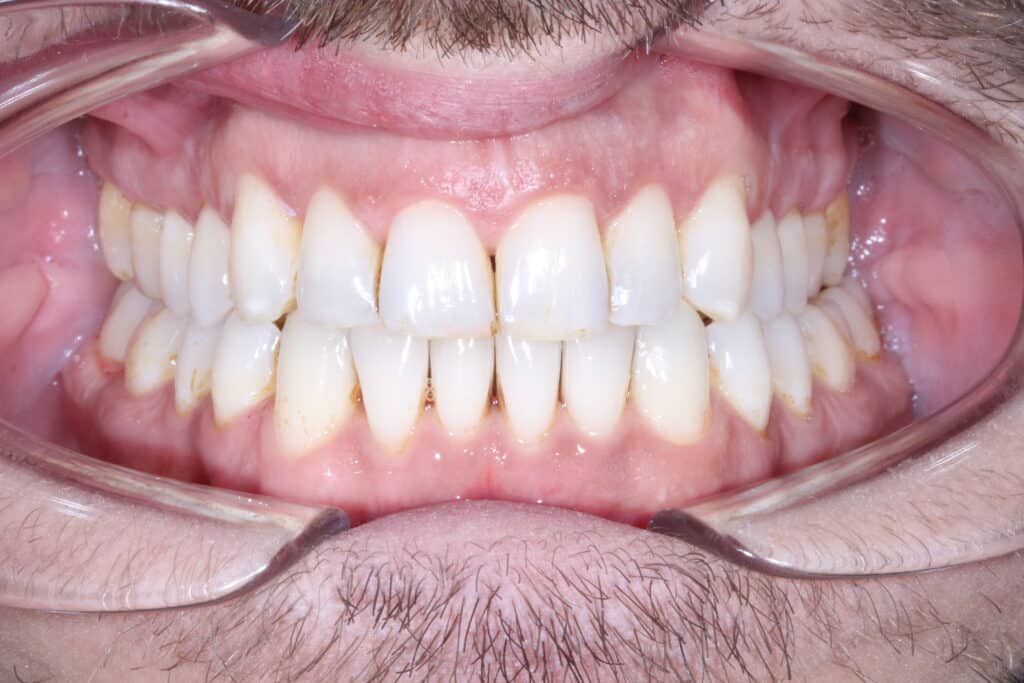
5. Re-evaluation.
Following this reassessment, what are the possible outcomes?
– The periodontal disease has stabilised and you are now entering a periodontal maintenance phase (dental hygiene sessions are simply more frequent than for an average patient).
– The disease has stabilised but the bone and gums destroyed by the disease need to be rebuilt (this is when the periodontal specialist comes into play).
– There are still a few active pockets and localised intervention is required (this is when the periodontal specialist comes into play).
Deep cleanings are carried out provided you can follow the instructions given by the hygienist at home (brushing technique, use of interdental brushes, etc).
What is periodontal disease and what are its symptoms?
Periodontal disease is a bacterial infection caused mainly by the accumulation of tartar under the gums, leading to inflammation of the gums and destruction of the supporting tissues around the teeth. It generally takes the form of gingivitis or periodontitis.
The symptoms are varied: bleeding from the gums, gradual recession of the gums, loosening (or even loss) of the teeth, teeth that start to move, the impression that the teeth are getting longer, bad breath, and so on.
What causes periodontal disease?
There are several possible causes of periodontal disease:
– Heredity;
– Inadequate oral hygiene;
– A major problem with dental alignment, which causes certain teeth to become overloaded;
– Extreme crowding, which means that the deposits between the teeth cannot be properly cleaned;
– The absence of molars, which means that chewing has to be compensated for by other front teeth;
– The presence of pockets of bacteria around the wisdom teeth;
– Regular and excessive consumption of alcohol and/or tobacco;
– Bad eating habits;
– Certain diseases (diabetes, HIV);
– Sudden hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause);
What are the risks of periodontal disease?
While periodontitis and gingivitis are relatively easy to treat, in some cases they can also lead to serious complications , including:
– Loosening or even loss of teeth;
– Cardiovascular or pulmonary disease;
– A direct impact on your diabetes;
– Premature childbirth, etc.
– Risk of the development of certain tumours.
What does non-surgical treatment of periodontal disease involve?
Non-surgical treatment of periodontal disease is carried out in several stages.
– Firstly, the hygienist carries out surface scaling to reduce inflammation. They will give you precise instructions to prevent your periodontitis or gingivitis from worsening.
-The dental practitioner will then measure the “periodontal pockets”, i.e. the amount of bone loss around each tooth.
– The hygienist or periodontologist will carry out deep cleaning with anaesthetic in 1 or 2 sessions: this involves removing the bacteria which is attached to the roots under the gums.
-A reassessment of the size of the pockets around each tooth is carried out to check the response to the periodontal treatment, after a healing period of 3 months.
Find out more about periodontal disease
How is periodontitis treated?
How do you get periodontitis?
How is severe periodontitis treated?
How should you brush your teeth if you have periodontitis?
When should you see a periodontist?
Can periodontitis be treated naturally?
What diet should you follow if you have periodontitis?
Surgical periodontics