Oral medicine and pathology
Oral medicine and pathology
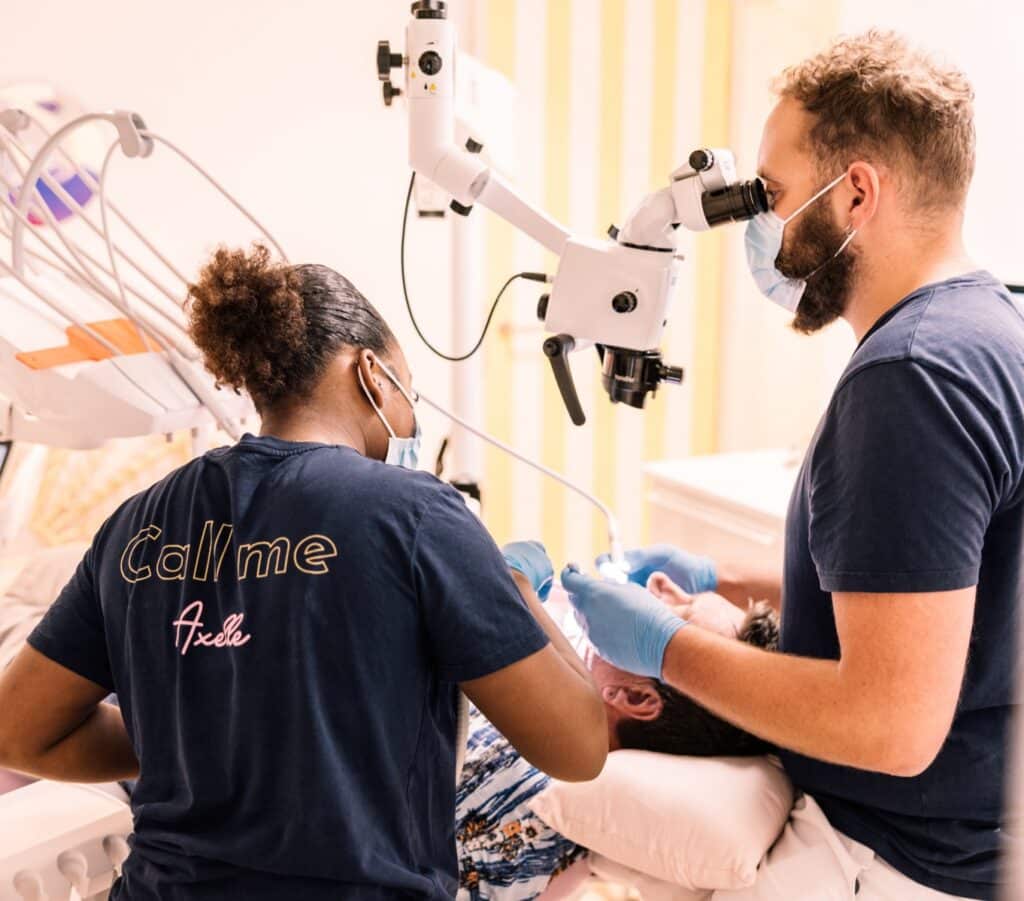
Oral medicine and pathology is the broadest speciality of dentistry, and is comparable to dermatology of the oral cavity.
Oral medicine and pathology at CHD
Lesions of the oral mucosa can have different aspects and origins. If you notice a change in your mouth, don’t hesitate to ask your dentist for a check-up. Prevention is better than cure!
Discover this treatment in video
Rates
| Oral medicine and pathology | .- |
Exact quotation before treatment.
*You can pay in installments.
Fair & transparent prices
We strive to maintain unbeatable value for money: reasonable prices, which have not changed since 2016, for quality of care that has earned us numerous awards:




Advice
When additional testing is carried out, it is sent to the laboratory to be analysed by a pathologist. Once the diagnosis has been made, your dentist will contact you to give you personalised advice and plan the next stage of your treatment.
It’s the least talked-about speciality of dentistry… and yet we are sometimes able to detect certain chronic diseases via “simple” initial oral lesions. It’s the very definition of prevention!
Dr Cante, Clinical Surgeon, CHD Geneva.
Next appointment
Your next appointment (recall) is scheduled as part of the personalised follow-up offered by CHD. This is based on your lifestyle, the quality of your saliva and other parameters, to ensure that your oral health remains at an optimum level. And you don’t have to worry about it any more, we’ll take care of reminding you: text message, letter, email, it’s your choice!
Our dental clinics
Find out more about oral pathologies
Oral medicine is a speciality of dentistry that involves diagnosing and treating diseases of the mouth. There are a number of symptoms that should prompt you to consult a surgeon specialising in oral pathology, particularly if you suffer repeated damage to the soft tissues (gums or tongue): ulcers, white or red spots, small bumps, etc. The appearance of a spot, swelling, etc. should also prompt you to consult a specialist.
An oral medicine and pathology consultation generally takes place in two stages:
– A thorough examination of the patient’s mouth;
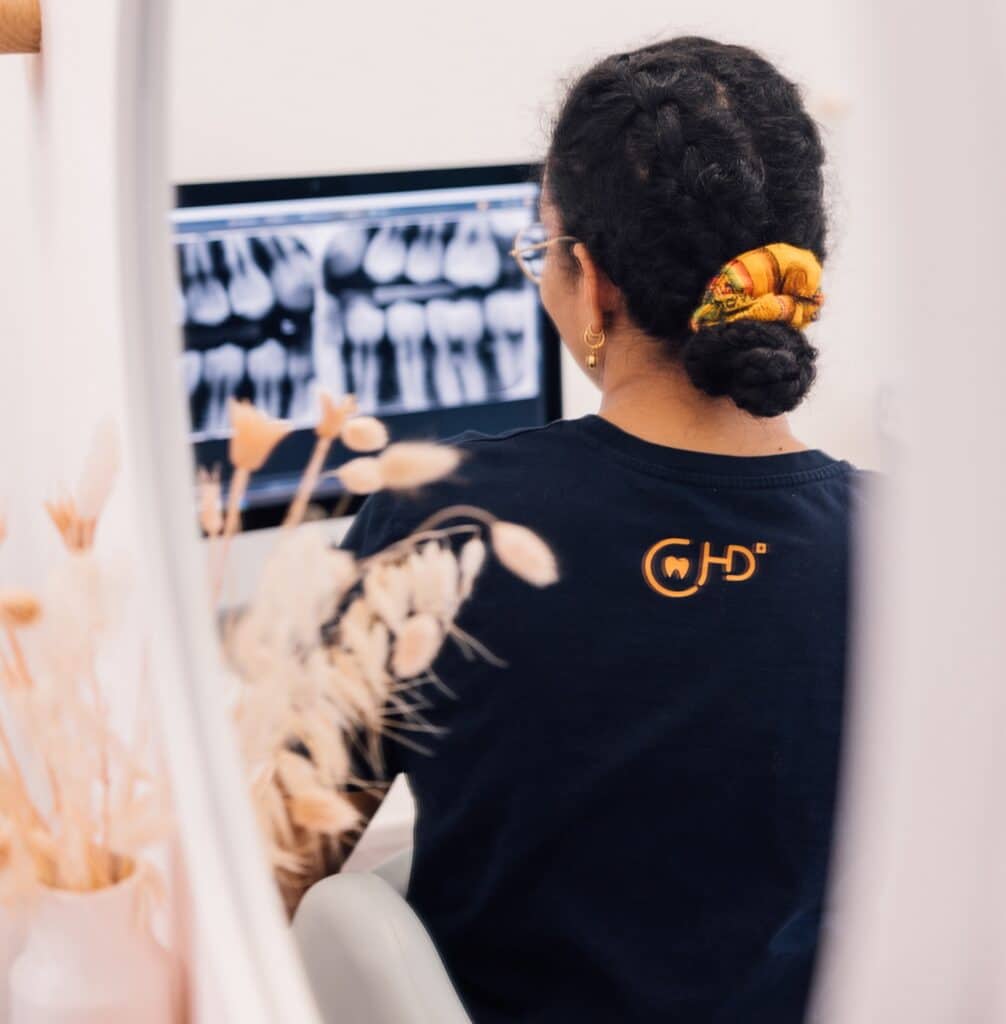
– Additional testings (biopsies, for example), which will be sent to the laboratory for analysis.
Once the diagnosis has been made by the surgeon specialising in oral pathology, the patient can begin the appropriate treatment.
Following the initial examination, the dentist may need to carry out additional examinations to establish his or her diagnosis more precisely, such as:
– A biopsy, which involves removing a small amount of tissue from the affected area;
– An excision, which involves removing the entire lesion from the oral mucosa.
Following these additional examinations, the samples are sent to the laboratory to be analysed by a pathologist.
The best way to prevent oral diseases is to practise good dental hygiene (brushing your teeth after every meal and using interdental brushes or dental floss) and to have regular check-ups with your dentist, so that he or she can check the state of your oral health and prevent the appearance of any oral diseases.
Depending on your predisposition, your dentist will also be able to advise you on the care you should take on a daily basis to limit the development of oral pathologies in your situation.
Finally, it should be noted that any irritant can lead to the development of oral lesions: tobacco (in any form, i.e. cigarettes, vapourisers, Snus, etc.), alcohol, medicines, drugs, or simply wounds that irritate the mucous membrane.